AR (Augmented Reality) is a technology that overlays digital content on the real world .
It is attracting attention as an element that improves the user experience in services in various fields, and in recent years, opportunities for general use such as smartphone apps and games are increasing.
In this article, we will explain the meaning of AR and the difference from VR in an easy-to-understand manner with examples of use.

What is AR (augmented reality)?
We will explain the meaning and basic knowledge of AR in detail.
Meaning of AR
AR (Augmented Reality) is translated as “augmented reality” in Japanese.
It is a technology that allows digital content such as navigation, 3D data, and videos to be superimposed on the real world through devices such as smartphones, AR goggles, and glasses .
Basic knowledge of AR
The concept of AR was born in the early 1900s. It was first proposed by novelist Lyman Frank Baum. However, AR research was systematized after the 1990s .
In 1992, the Armstrong Air Force Research Laboratory in the United States developed ” Virtual Fixtures ” and conducted demonstrations to improve the operational capabilities of aircraft pilots. At the same time, Columbia University announced KARMA , an AR system for laser printer maintenance support .
In 1999, Mr. Hirokazu Kato of the Nara Institute of Science and Technology developed the AR application library ” ARToolkit “, greatly reducing the cost of the technology and greatly contributing to the spread of AR.
In the 2000s, AR began to be widely used in commercial products for general consumers such as games, apps, and wearable devices.
In 2007, Sony released the game “THE EYE OF JUDGMENT” using AR. In addition, “ Pokémon GO ” released in 2016 became a global hit with 850 million downloads in two years.
AR type
AR is broadly classified into four types.
Location-aware (GPS) type AR
Location-based AR is a technology that acquires location information from the GPS installed in smartphones, etc., and displays AR content linked to the location information .
It has been incorporated into navigation services such as MAP and game applications that utilize location information such as “Pokémon GO”.
Image recognition (marker) type AR
Image recognition type AR is a technology that sets specific images, buildings, etc. as markers, and displays AR content such as 3D and video when the markers are recognized (the characteristics match) .
It is often used in promotions and events such as product packages.
Object recognition (non-marker) type AR
Object recognition type AR is a technology that displays AR content when a specific three-dimensional object is recognized . Similar to image recognition, a camera analyzes the feature points of a three-dimensional object, but object recognition AR can recognize three-dimensional objects from anywhere in 360 degrees.
It is used not only in products for general consumers such as product packages and figures, but also in situations such as machine maintenance and work efficiency improvement in the manufacturing industry.
Spatial recognition type AR
Spatial recognition type AR is a technology that can be activated simply by tapping the screen of a device such as a smartphone. By recognizing the space in the real world, you can freely display AR content on the floor or on the desk .
It is used to improve operational efficiency in fields such as simulation and fitting applications such as IKEA’s furniture placement simulation application, manufacturing industry, and construction industry.
Differences from VR/MR/XR
We will explain in detail the differences between VR, which is often talked about together with AR, and MR and XR, which have been attracting attention in recent years.
Difference from VR (Virtual Reality)
VR is translated as virtual reality in Japanese. A technology that allows you to wear a wearable device for VR and experience a virtual space .
While AR is a technology that displays virtual data in the real world, VR has a difference in that it provides a realistic experience as if you were in a virtual space. The greatest feature of VR is the immersive feeling of being in another world.
Difference from MR (Mixed Reality)
MR is translated as mixed reality in Japanese. A technology that displays CG in the real world by wearing a wearable device dedicated to MR .
It is very similar to AR, but in MR, it is possible not only to display virtual data, but also to touch the data and perform operations and rewrite information. In addition, multiple people can experience it at the same time.
Differences from XR (Extended reality)
XR (Extended Reality) is a general term that represents all technologies that fuse the real world and the virtual world to make it possible to perceive things that do not exist in reality . In other words, technologies such as AR, VR, and MR are all concepts included in XR.
Behind the birth of the word XR, many technologies that combine AR and VR technologies continue to be created, and the recent trend that the boundaries between each technology is becoming ambiguous has had a major impact. increase.
AR use cases (by industry)
We will introduce examples of AR utilization by industry.
Retail: IKEA Place
IKEA, a leading Nordic furniture maker, has jointly developed an application “ IKEA Place ” that allows you to place furniture in a room with AR.
By using IKEA Place, you can place digital furniture in the room via your smartphone, check the size of the product, and simulate the matching atmosphere with the surroundings.
Game: Pokemon GO
“Pokemon GO” is a location information game application for smartphones developed by Niantic. Since its release in 2016, it has become a worldwide hit.
In this game, you can use location information to move to various locations, capture nearby Pokémon, train them with the items you collect, and battle other users.
Sports: HADO
“HADO” is an indoor sport that utilizes AR.
Equipped with a head-mounted display and arm sensor, you can experience as if you were activating energy balls and shields using AR with your own hands.
Art: Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution has developed an application called “Skin & Bones” that displays the original appearance of animals and fish when they were alive, simply by comparing the skeletal specimens on display with the camera of a smartphone or tablet.
You can also enjoy commentary videos and 3D images by loading the images in the Bone Hall in the museum.
Logistics: DHL
DHL, a major international transportation company, uses Google Glass as a picking support tool.
By displaying the storage location and necessary information on Google Glass, it is no longer necessary to work while holding documents, and we have succeeded in improving work efficiency.
Agriculture: Huxley
Huxley has developed an AI-powered crop management system.
By using this service, AI detects various risks related to growing crops and displays the information on wearable devices.
Monster Lab’s AR utilization example
We will introduce the achievements of various digital product development utilizing Monster Lab’s AR.
Gardens by the Bay (Route guidance function of the official app)
Monster Lab participated in the renewal of the official app of Singapore’s famous theme park “Gardens by the Bay” from the research and planning phase. We supported the promotion of DX by improving UX using technology .
The client’s issues are not only the UX and contents of the application, but also the user experience in the park, such as “congestion when purchasing admission tickets or entering the park”, “bias of crowded time zone”, “crowding of popular attractions”, and “lack of guidance in the park”. It covered a wide range of things related to
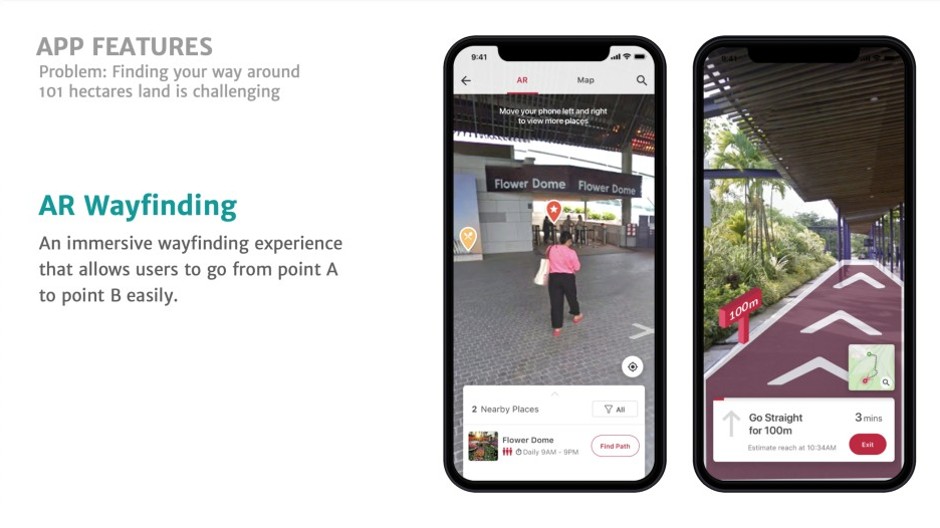
Introduced a route guidance function using AR as a solution to the lack of guidance in the park
Monster Lab not only creates a UX that makes people want to go to the site by improving the app, but also provides various solutions to problems. As a solution to the “lack of guidance in the park”, we have introduced a route guidance function that utilizes AR .

Kubota (failure diagnosis app)
Kubota, a major manufacturer of construction and agricultural machinery, is expanding its products globally.
The problem was that construction equipment repairs, which were carried out by service engineers at local distributors, could not be supported with manuals alone, depending on the experience and skills of the person in charge.
A decrease in the operating rate of construction equipment due to downtime is directly linked to a decrease in user profits. Therefore, there was a need for quick, efficient, easy-to-understand failure diagnosis support that is not dependent on the ability of service engineers.
Monster Lab has developed a fault diagnosis app as a solution to these problems. We built a simple failure diagnosis flow that displays inspection points and repair methods just by entering an error code or problem symptom .
In addition, by combining 3D models and AR, by holding up a smartphone, it is equipped with a function that allows you to visually recognize the location of failures inside the construction machine and the identification of target parts, saving you the trouble of actually checking the inside of the machine.

Conclusion: Leverage AR to improve user experience
AR is a technology that displays digital content in the real world through smartphones and wearable devices.
Currently, it is incorporated into services in various fields and is used for entertainment and work efficiency.
By utilizing AR for new businesses and services, create a new user experience that cannot be achieved with content only on the web, and improve customer satisfaction.
