If you have duplicate or similar pages, you should indicate which pages you want search engines to rate with canonical tags. This is called “URL normalization” and is one of the basic measures of SEO.
However, URL canonicalization varies depending on the case, such as 301 redirects without canonical tags.
Therefore, in this article, we will explain the correct usage of canonical tags, points to note, and the importance of URL normalization.
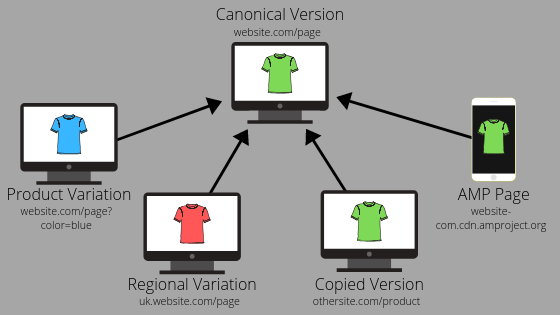
Table of Contents
- About canonical tags and URL canonicalization
- How to normalize using the canonical tag
- 4 situations where you should use canonical tags
- Notes on using canonical tags
- URL normalization for flawless SEO
About canonical tags and URL canonicalization
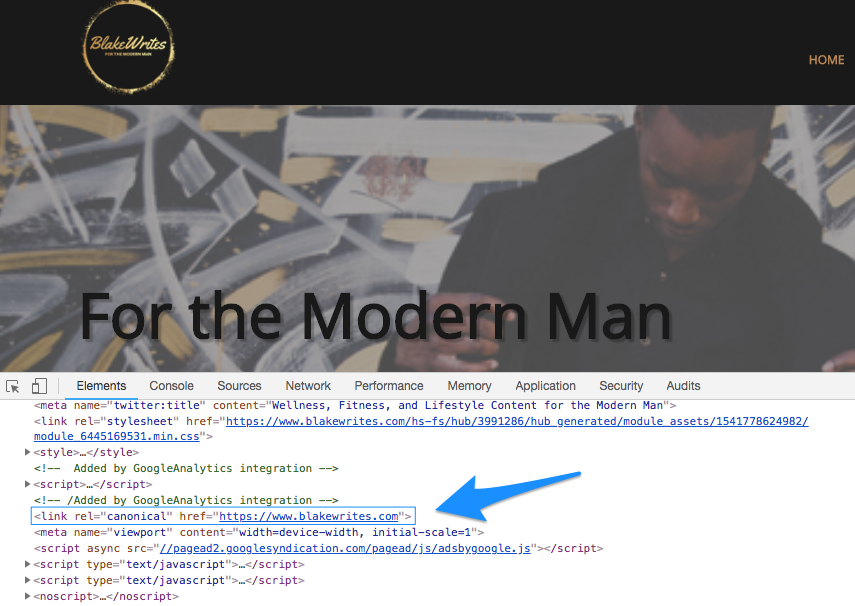
A canonical tag is a tag th indicates a canonical URL that you want search engines to evaluate when there is duplicate content or content with almost the same content on the site .
For example, duplication or similar pages are often generated when running a site, such as the presence or absence of “www” and “index.html”. In such cases, we use canonical tags in order to combine the evaluations from search engines into one page without distributing them.
However, since search engines only take the canonical tag as a hint, pages other than the specified page may be indexed as canonical pages.
The canonical tag is written inside the head element of HTML.
There are two main purposes for using canonical tags: 1. Integrate the evaluations of two or more pages with the same content into one, and 2. Crawl the canonical page preferentially.
Regarding “1. Combine the evaluations of two or more pages with the same content into one”, if there are multiple pages with the same content, the inflow and clicks from the search results will be dispersed, and the external Links may be created and the evaluation of the page from Google may be dispersed.
By using the canonical tag, these scattered evaluations can be unified into a canonical page.
Regarding “2. Crawl the canonical page preferentially”, using the canonical tag makes it easier for the crawler to crawl the canonical page preferentially, which may shorten the crawl time within the site. .
The reason why you need to set the canonical tag is that even if the content is exactly the same, if the URL is different, the search engine treats it as a different page .
For example, we humans think that the two URLs “http://www.hubspot.jp” and “http://hubspot.jp” point to exactly the same page. Even on the actual HubSpot website, these two URLs point to the same page, and the different URLs simply represent different ways to access the page.
Even though the URL is different like this, the user understands that it is the same page.
However, search engines recognize the difference in URLs as a difference in pages, and therefore determine that these two URLs are different pages.
URL canonicalization solves this problem.
About 301 redirects
A 301 redirect is the permanent transfer of one URL to another .
For example, say you 301 redirected “example.com” to “www.example.com”. In this case, accessing “example.com” will automatically redirect to “www.example.com”. A 301 redirect tells users and Google that the page has been permanently redirected to the destination URL.
301 redirect is used when you move to the destination page as follows and you no longer use the original page or access is no longer required.
————————————————–
- When you move your site to a new domain
- When you merge two sites and no longer need access to one site
- If you want to delete the content in the page and transfer it to a new page
- When there are multiple URLs that users access
(http://example.com/home, http://home.example.com, etc.)
————————————————–
As you can see from the example above, the contents of the destination page and the original page (the page being transferred) are not always the same .
On the other hand, canonical is used to specify one URL as the canonical URL when two or more URLs are generated for some reason, even though the content is the same.
For more information about 301 redirects, please refer to Google’s official page ” Redirects and Google Search “.
How to normalize using the canonical tag
There are several ways to normalize website URLs.
Each method has its pros and cons, and which one is best for your company depends on your overall web strategy.
Use <link rel=”canonical”> tags
The biggest advantage of this method is that there is no upper limit to the number of canonical URLs you can specify, and you don’t have to worry about URL paths .
Note that this method cannot be used to normalize PDF files that do not have data in HTML. (PDF files can be canonicalized by the method of “Using rel=canonical in the HTTP header” introduced next.)
By the way, in CMS such as WordPress and HubSpot, canonical tags are automatically set when content is created, and automatically updated when the URL is changed.
Use rel=canonical in HTTP headers
Similar to the <link rel=”canonical”> tag, you can specify the exact canonical version of your content by setting the canonical URL in the HTTP response header .
As mentioned in the previous item, canonical tags inside the HTML head tag only work on HTML pages.
For files such as PDFs that are not HTML data, use HTTP response headers to specify which files are regular files.
As with the tag method, there is no limit to the number of pages you can specify with this method.
However, it has the disadvantage of being slightly more difficult to set up than other methods and difficult to maintain for large websites or sites with frequently changing URLs.
4 situations where you should use canonical tags
The previous example of the same content posted on http://www.hubspot.jp and http://hubspot.jp is just one of the cases where URL canonicalization is important.
Common situations where URL canonicalization is necessary include:
Have AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) or mobile pages
When creating mobile content, you may create a subdomain as shown below and create a mobile page or AMP page with the same content as the PC page.
————————————————–
https://example.com/news/koala-rampage (PC page)
https://m.example.com/news/koala-rampage (Smartphone page)
https://amp.example.com/news/ koala-rampage (AMP page)
——————————————– ——-
In this case, normalization is required so that it is not considered a duplicate page.
If you want the PC page to be the canonical URL, insert the canonical tag as follows in the HTML head tag of the smartphone page and AMP page.
————————————————–
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/news/koala-rampage” />
———————— ————————–
In addition, when normalizing the smartphone page to the PC page, insert the attribute “alternate” in the HTML head tag of the PC page as shown below to indicate that there is a smartphone page other than the PC page. Google recommends as shown.
————————————————–
<link rel=”alternate” media=”only screen and (max-width: 640px)”href=”https://m.example.com/news/koala-rampage”>
——— —————————————–
Multiple URLs are generated for the same product on an EC site, etc.
On EC sites, even for the same product, different pages may be generated by adding “parameters (character strings after “?”)” to the URL depending on the type of product, such as color or size.
For example, let’s say you have a website that sells dog toys. If the best-selling toy has multiple color variations, the URL should be set according to each color, as shown below.
————————————————–
● Blue product introduction page
example.com/product?color=blue
● Green product introduction page
example.com/product?color=green
—————— ——————————–
If for some reason you want the blue product introduction page to be the canonical URL, insert a canonical tag into the HTML of the green product introduction page “example.com/product?color=green”.
However, by normalizing multiple variations of a page to a single page, the other pages will not appear in search results. Doing so prevents users looking for a product in a particular color or size from finding that product page in search results.
Therefore, unless you have a clear reason to want to canonicalize to this page, do not normalize multiple variations and leave them as individual pages.
Separate URLs for each region and country
For pages in a multilingual or multiregional site, if the language used is the same and the content of the page does not change but there are different URLs, normalize them.
————————————————–
https://example.de/ (page with subdomain)
https://example.com/de/ (page in different hierarchy)
—————– ———————————
Note that different languages or different page content are not considered duplicate content and do not require normalization.
If you operate a multi-language or multi-region site, please proceed with normalization while referring to the Google Developers page ” Multi-region, multi-language site | Google Search Central | Documents | Google Developers “.
About self-referencing URLs
Until now, the usage of the canonical tag was to insert the canonical tag into the URL “A” to be canonicalized when there was a URL “B” with the same content as the URL “A” to be canonicalized. Another technique is to insert tags.
This is sometimes called ” self-referential canonical “.
For example, when content is created with a CMS such as WordPress, a canonical tag that specifies the URL of the page itself may be automatically inserted into the HTML of that page.
By specifying your own page as the regular URL in advance, for example, even if a URL with parameters (character string after “?”) is generated for mail magazine distribution as shown below, those URLs You can collect the evaluation to canonical URL.
————————————————–
http://www.example.com/de (regular URL)
http://www.example.com/de?utm_source=magagine (URL for e-mail magazine distribution)
————- ————————————-
Notes on using canonical tags
As we have introduced so far, setting canonical tags is an important measure for SEO, but please be aware of the following points when setting them.
Make the first page of content that spans multiple pages the canonical URL
Especially when creating a page with a large amount of content, it may be divided into multiple pages and published.
At that time, there are cases where the URL of the first page is specified with a canonical tag to make it a canonical URL, but it is a wrong measure because the contents of the first and second pages are different.
In this state, the second and subsequent pages will not be found by the crawler and will not be displayed in the search results at all.
Write a relative URL
Canonical tags must be absolute URLs. For example, if you want “https://example.com/news/koala-rampage” to be the canonical URL, the tag description would be as follows.
<link rel=canonical href=“https://example.com/news/koala-rampage” />
On the other hand, the following description will be a relative URL because the “https://” at the beginning is missing.
<link rel=canonical href=“example.com/news/koala-rampage” />
If you describe it like this, the crawler will recognize the canonical URL as “https://example.com/example.com/news/koala-rampage”, and the canonical tag will be specified as if this page does not exist. Ignored.
Even with the same relative URL, the following description will be properly recognized as “https://example.com/news/koala-rampage”, but it is recommended to write an absolute URL to prevent mistakes.
<link rel=canonical href=“news/koala-rampage” />
URL normalization for flawless SEO
Having a canonical URL on your website helps your site visitors and search engines know exactly where your content is.
Leverage URL canonicalization to show the structure of your content correctly while maximizing your SEO traffic.